AngularJS is a powerful JavaScript framework that allows developers to build dynamic web applications with ease. One of its key features is the routing module, which enables the creation of single-page applications (SPAs) with multiple views.
We will build an application that displays the framework details using AngularJS routing.
Refer to the following gif to generate the required output.
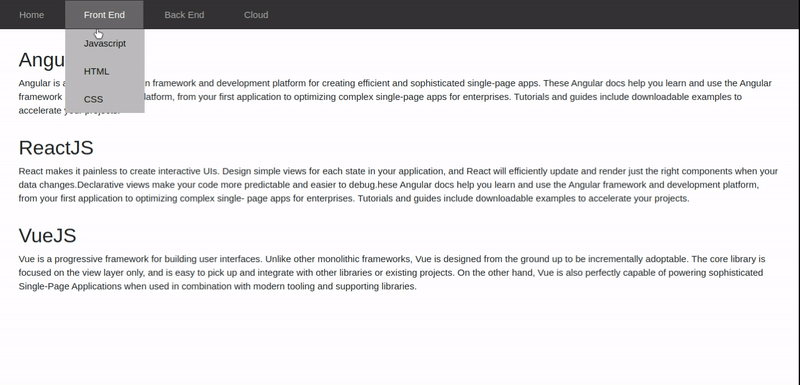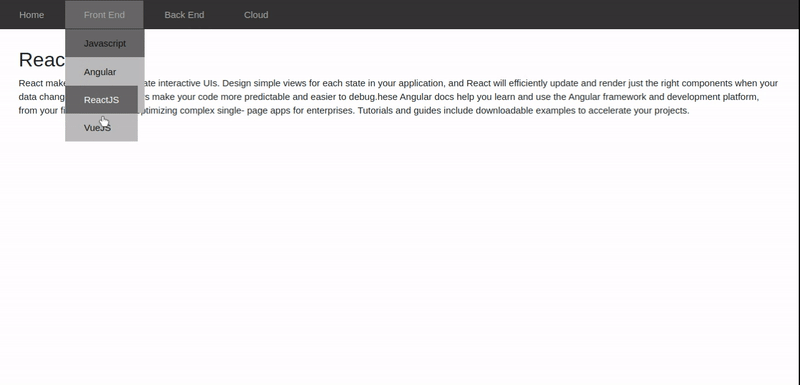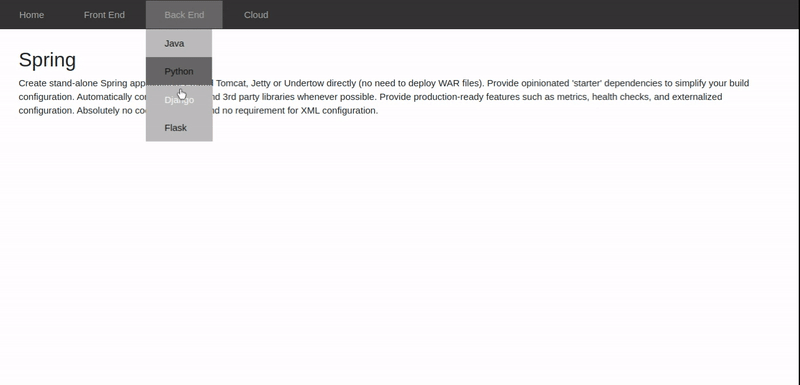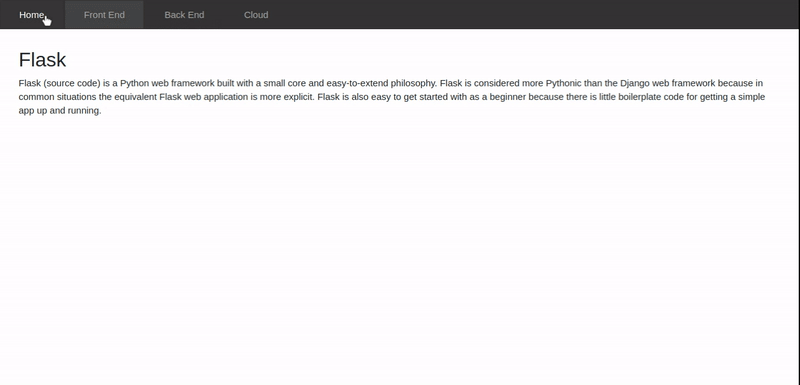
In this tutorial, we will build an application that displays details about various front-end and back-end frameworks using AngularJS routing.
Before we dive into the code, let's set up our project and understand its structure.
Project Structure
1. `index.html`: The main HTML file that loads the AngularJS framework and includes necessary scripts.
2. `app.js`: The main AngularJS module and configuration for routing.
3. `controllers.js`: Contains the controller definitions for different views.
4. `templates/`: Folder containing the HTML templates for each view.
Building the Navigation Bar
Let's start by creating the navigation bar in the `main.html` file. This navigation bar will contain links to different framework pages.
Complete main.html file code.
<div ng-controller="MainController">
<nav>
<ul>
<li class="top-menu">
<!--navigate to 'intro.html'-->
<a ng-href="/">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="top-menu">
<!--navigate to 'front-end.html'-->
<a ng-href="/front-end" id="route-front">Front End</a>
<ul>
<li class="front-end-menu1">
<a href="#js">Javascript</a>
<ul>
<!--navigate to 'front-end.html' with route param as 'angular'-->
<li><a ng-href="/front-end/angular" id="front-ang">Angular</a></li>
<!--navigate to 'front-end.html' with route param as 'react'-->
<li><a ng-href="/front-end/react" id="front-react">ReactJS</a></li>
<!--navigate to 'front-end.html' with route param as 'vue'-->
<li><a ng-href="/front-end/vue" id="front-vue">VueJS</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="front-end-menu2">
<a href="#web">HTML</a>
</li>
<li class="front-end-menu3">
<a href="#web">CSS</a>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="top-menu">
<!--navigate to 'back-end.html'-->
<a ng-href="/back-end" id="route-back">Back End</a>
<ul>
<li class="back-end-menu1">
<a href="#java">Java</a>
<ul>
<!--navigate to 'back-end.html' with route param as 'spring'-->
<li><a ng-href="/back-end/spring" id="back-spring">Spring</a></li>
<!--navigate to 'back-end.html' with route param as 'hibernate'-->
<li><a ng-href="/back-end/hibernate" id="back-hiber">Hibernate</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="back-end-menu2">
<a href="#python">Python</a>
<ul>
<!--navigate to 'back-end.html' with route param as 'django'-->
<li><a ng-href="/back-end/django" id="back-django">Django</a></li>
<!--navigate to 'back-end.html' with route param as 'flask'-->
<li><a ng-href="/back-end/flask" id="back-flask">Flask</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li class="top-menu">
<a href="#cloud">Cloud</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#microsoft">Microsoft Cloud</a></li>
<li><a href="#google">Google Cloud</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
In the above code, we've created anchor links for each framework category and its subcategories. The `ng-href` attributes are set according to the desired routes.
Displaying Introduction Details
Now, let's work on the `intro.html` template and the corresponding `IntroController`. This section will display general information about the application.
Complete intro.html file code.
<div ng-controller="IntroController">
<!-- include the main.html page using ng-include -->
<ng-include src="'main.html'"></ng-include>
<h1>About</h1>
<!-- iterate the intros array in following article tag -->
<article id="intro-details" ng-repeat="intro in intros">
<h2>{{intro.heading}}</h2>
<p>{{intro.description}}</p>
</article>
</div>
In the above code, we've included the `main.html` page using `ng-include` and iterated through the `intros` array to display the introduction details.
Displaying Front-End and Back-End Framework Details
Next, we'll create templates and controllers for the front-end and back-end framework details pages.
Complete front-end.html file code
<div ng-controller="FrontEndController">
<!-- include the main.html page using ng-include -->
<ng-include src="'main.html'"></ng-include>
<!--
iterate the frontends array in following article tag
filter the arrays using tech from route param
-->
<article id="front-end-techs" ng-repeat="frontend in frontends | filter: { heading: by_tech }">
<h2>{{frontend.heading}}</h2>
<p>{{frontend.description}}</p>
</article>
</div>
The `FrontEndController` fetches the route parameter `tech` and uses it to filter the front-end frameworks accordingly.
Similarly, we'll create the template and controller for the back-end framework details page.
Complete back-end.html file code
<div ng-controller="BackEndController">
<!-- include the main.html page using ng-include -->
<ng-include src="'main.html'"></ng-include>
<!--
iterate the backends array in following article tag
filter the arrays using tech from route param
-->
<article id="back-end-techs" ng-repeat="backend in backends | filter: {heading: by_tech}">
<h2>{{backend.heading}}</h2>
<p>{{backend.description}}</p>
</article>
</div>
Configuring Routing
Finally, let's configure the routing in the `app.js` file.
Complete main.js file code
var app = angular.module("myApp", ["ngRoute"]);
app.run(function ($rootScope) {
$rootScope.deviceName;
});
// Main Controller - Don't modify or delete this Main Controller
app.controller("MainController", function ($scope, $location, $rootScope) {
$scope.init = function () {
}
$scope.init();
});
// Intro Controller - Don't modify or delete this Intro Controller
app.controller("IntroController", function ($scope, $location, $rootScope) {
$scope.init = function () {
// default data - don't delete or modify this
$scope.intros = [
{
heading: "Know IT",
description: "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Aliquam ut ipsum posuere, rutrum neque ac, sodales lacus. Vivamus in est aliquam, varius odio vitae, consequat nibh. Nunc metus justo, euismod nec commodo hendrerit, faucibus sit amet nulla. Maecenas gravida hendrerit laoreet. Pellentesque luctus mauris sapien, ac consequat diam mollis et. Nulla quis molestie sem. Quisque et tempus lacus. Integer dui lacus, pretium a efficitur non, ornare sed dui. Ut sit amet neque vitae ipsum lacinia auctor. Maecenas tellus mi, maximus sodales ultricies id, aliquam ac mi. Proin nulla justo, venenatis id diam quis, porttitor tincidunt urna. Donec lobortis vel felis vitae placerat. Suspendisse eget lectus urna. Proin nec ex vitae diam ultricies pretium vitae non sem. Proin quis nulla ut justo pharetra aliquet sed quis est. Donec pulvinar tortor eros, sit amet elementum est aliquet eget."
},
{
heading: "Know IT",
description: "Pellentesque eget tincidunt diam. Sed volutpat libero id tristique luctus. Cras viverra sagittis ipsum ac porta. Nunc congue est sit amet purus ornare, vel suscipit mi varius. Cras rutrum vehicula lacus, et dictum ligula pharetra ut. Aliquam tempus, lorem in gravida fermentum, dui ex efficitur ipsum, vitae gravida dolor purus ac nisl. Ut a tellus sit amet elit efficitur porttitor. Vestibulum sit amet sagittis libero, in eleifend nisi. Mauris molestie gravida eros quis blandit."
},
{
heading: "Know IT",
description: "Donec dolor elit, vestibulum vel tempor vitae, dignissim in libero. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Donec eleifend libero eu pharetra rutrum. Phasellus massa, quis sollicitudin lorem lectus ac lectus. Fusce pellentesque orci ut tincidunt accumsan. Vestibulum dictum, lorem eu aliquet bibendum, turpis ex cursus ex, sed ultricies ex est ut nisl. Phasellus metus risus, euismod imperdiet malesuada at, finibus ut lacus. Nam convallis auctor eros, et efficitur neque tristique ut. Vivamus velit neque, ornare eget erat id, finibus dictum tortor. Nunc varius fermentum nibh nec tempor. Maecenas ut maximus dolor. Aliquam a ipsum mi. Suspendisse porta ante vitae felis facilisis, in accumsan tortor efficitur. Class aptent taciti sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. Phasellus pharetra cursus lacus, sed dapibus sem lobortis sit amet."
}
]
}
$scope.init();
});
// FrontEnd Controller - Don't modify or delete this Main Controller
app.controller("FrontEndController", function ($scope, $routeParams, $location, $rootScope) {
$scope.init = function () {
// if there is an route param, assign the value into the variable "by_tech"
$scope.by_tech = $routeParams.tech;
// default data - don't delete or modify this
$scope.frontends = [
{
heading: "Angular",
description: "Angular is an application design framework and development platform for creating efficient and sophisticated single-page apps. These Angular docs help you learn and use the Angular framework and development platform, from your first application to optimizing complex single-page apps for enterprises. Tutorials and guides include downloadable examples to accelerate your projects."
},
{
heading: "ReactJS",
description: "React makes it painless to create interactive UIs. Design simple views for each state in your application, and React will efficiently update and render just the right components when your data changes.Declarative views make your code more predictable and easier to debug.hese Angular docs help you learn and use the Angular framework and development platform, from your first application to optimizing complex single- page apps for enterprises. Tutorials and guides include downloadable examples to accelerate your projects."
},
{
heading: "VueJS",
description: "Vue is a progressive framework for building user interfaces. Unlike other monolithic frameworks, Vue is designed from the ground up to be incrementally adoptable. The core library is focused on the view layer only, and is easy to pick up and integrate with other libraries or existing projects. On the other hand, Vue is also perfectly capable of powering sophisticated Single-Page Applications when used in combination with modern tooling and supporting libraries."
}
];
}
$scope.init();
});
// BackEnd Controller - Don't modify or delete this Main Controller
app.controller("BackEndController", function ($scope,$routeParams, $location, $rootScope) {
$scope.init = function () {
// if there is an route param, assign the value into the variable "by_tech"
$scope.by_tech = $routeParams.tech;
// default data - don't delete or modify this
$scope.backends = [
{
heading: "Spring",
description: "Create stand-alone Spring applications. Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files). Provide opinionated 'starter' dependencies to simplify your build configuration. Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible. Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration. Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration."
},
{
heading: "Hibernate",
description: "Hibernate ORM is concerned with helping your application to achieve persistence. So what is persistence? Persistence simply means that we would like our application’s data to outlive the applications process. In Java terms, we would like the state of (some of) our objects to live beyond the scope of the JVM so that the same state is available later."
},
{
heading: "Flask",
description: "Flask (source code) is a Python web framework built with a small core and easy-to-extend philosophy. Flask is considered more Pythonic than the Django web framework because in common situations the equivalent Flask web application is more explicit. Flask is also easy to get started with as a beginner because there is little boilerplate code for getting a simple app up and running."
},
{
heading: "Django",
description: "Django is a high-level Python Web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. Built by experienced developers, it takes care of much of the hassle of Web development, so you can focus on writing your app without needing to reinvent the wheel. It’s free and open source."
}
];
}
$scope.init();
});
Complete routingConfig.js file code
// Define routes with corresponding html and controller
// for "/" - route to intro.html
// for "/front-end" or "/front-end/:tech" - route to front-end.html - tech is route parameter
// for "/back-end" or "/front-end/:tech" - route to back-end.html - tech is route parameter
// Note: should redirect to intro.html by default or other routes
app.config(['$routeProvider', '$locationProvider', function ($routeProvider, $locationProvider) {
// Define your routes here
$locationProvider.html5Mode(true);
$routeProvider
.when('/', {
templateUrl: 'intro.html',
controller: 'IntroController'
})
.when('/front-end', {
templateUrl: 'front-end.html',
controller: 'FrontEndController'
})
.when('/front-end/:tech', {
templateUrl: 'front-end.html',
controller: 'FrontEndController'
})
.when('/back-end', {
templateUrl: 'back-end.html',
controller: 'BackEndController'
})
.when('/back-end/:tech', {
templateUrl: 'back-end.html',
controller: 'BackEndController'
})
.otherwise({
redirectTo: '/'
});
}]);
In this code, we've defined different routes for introduction, front-end, and back-end pages. We've also set up routes with a parameter for specific framework categories.
Running the Application
To run the application, you can follow these steps:
1. Create the project structure as described earlier.
2. Include the required AngularJS scripts in your `index.html` file.
3. Set up the routing configuration in your `app.js` file.
4. Create the necessary controllers in your `controllers.js` file.
5. Create the templates (`intro.html`, `front-end.html`, `back-end.html`) in the `templates` folder.
6. Run your application using a local server or an online IDE.
By following these steps, you'll have a fully functional AngularJS application that displays framework details using routing. Users can navigate between different framework categories and even filter frameworks based on specific technologies. This project demonstrates how AngularJS routing can be used to create a seamless SPA experience for users.




